How to choose a car disk
 When choosing car disks It should be remembered that the width of the rim should be 25-30% less than the width of the profile of the tire. If you need a drive for a bus 195/70 R15, then the calculation is as follows: take the width of the profile in inches (195 mm divide by 25.4) = 7.68 - (25% or 30%) and the resulting number is rounded to the nearest value from the standard row. As a result of such calculations, you will get a value of 5.5. A rim of this width is needed for the 195/70 R15 tire.
When choosing car disks It should be remembered that the width of the rim should be 25-30% less than the width of the profile of the tire. If you need a drive for a bus 195/70 R15, then the calculation is as follows: take the width of the profile in inches (195 mm divide by 25.4) = 7.68 - (25% or 30%) and the resulting number is rounded to the nearest value from the standard row. As a result of such calculations, you will get a value of 5.5. A rim of this width is needed for the 195/70 R15 tire.Use both too wide and toonarrow discs (relative to the width of the profile of the tire) is undesirable: the design profile of the tire is broken (the sidewalls are either compressed by rim flanges or stretched over it), which is why its driving characteristics are deteriorated - reaction to rotation, resistance to slip, lateral rigidity. The permissible deviation of the rim width from the norm is 0.5 - 1.0 inches for disks with a mounting diameter of up to 14 inches; and 1.0 - 1.5 inches - for discs with a diameter of 15 inches or more. But it's better, of course, to take the disk exactly under the bus.
Recently, there has been a steady trend towardsincrease in mounting diameter; machines for which are regular, for example, 13-inch disks, translate to 14-inch, 15 to 16, etc. This is due to the desire to use tires of low and ultra-low series, as their driving qualities are better than high-profile tires. And the lower the tire series, the less rubber in the wheel and, correspondingly, more metal - after all the outer diameter of the wheel remained unchanged. When using steel wheels, the mounting diameter will not be increased significantly - this will lead to an increase in the mass of the wheel, which is undesirable. And the use of light alloy wheels allows you to increase the mounting diameter of the disk, without heavier wheel as a whole.
Do not put wheels with a non-standarddeparture. Reducing the outreach makes the wheel track wider; although it is a little and increases the stability of the car and gives it a stylish racing look, but at the same time sharply overloads the bearings of the hubs and suspension. Increase the crash, i.e. narrow the track, as a rule, impossible - the disk rests against the brake.
The main dimensions of the disk:

- A is the width of the disc, indicated in inches
- R is the diameter of the disk
- ET - departure, i.e. distance from the central axis of symmetry of the disk to the plane of contact of the disk to the hub (it can be both positive and negative, then the wheel is in contact with the hub to the left of the axis of symmetry)
- Q - number of fastening holes - number of bolts on which the disk is attached
- D is the diameter of the central hole of the disk
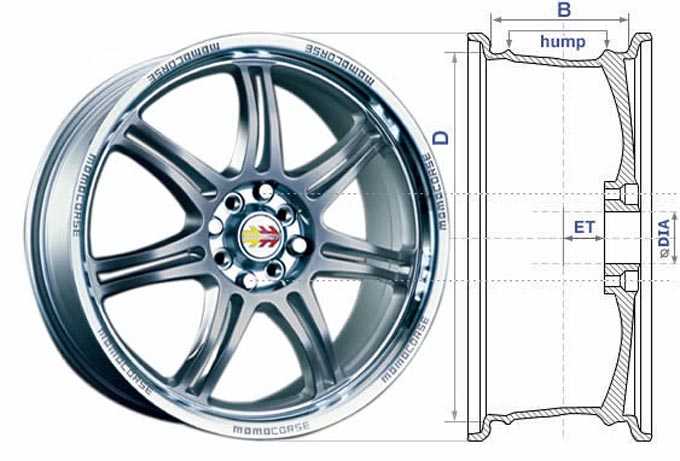
Explanation of the marking of wheel disks:
When choosing car disks in their markings, it's easy to get confused. All dimensions are in inches.
Example of marking of disks: 6,5xR16 / 6 * 139 / ET20 / d98,5
- 6.5 - wheel rim width in inches
- R16 is the rim diameter in inches
- 6 - number of fastening bolts
- 139 - discrepancy (distance) between fixing bolts
- ET20 - reach 45mm
- d98,5 - the diameter of the central hole on which the disc is placed
The width and diameter are chosen in accordance withthe size of the tire. To determine the overall width of the wheel rim, add to the value of the width of the rim on the marking of another 26 mm. thickness of the outer and inner side beads. The overall width of the rim should be 12 ± 4 millimeters less than the width of the tire profile.













