Stomatitis in infants

Babies often suffer from the same diseases as adults, but only suffer much more difficult, because the baby's body is still so fragile! So, stomatitis in infants delivers many unpleasant minutes to the children themselves and their parents.
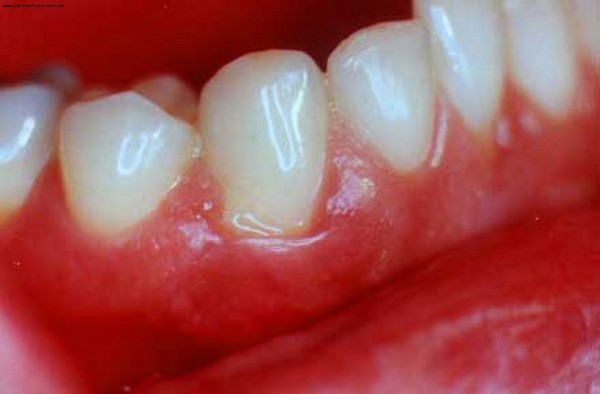
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. Symptoms of stomatitis - edema of the mucosamouth, pain, increased saliva. Sometimes the mucous membrane becomes covered with yellow or white coating, bleeding gums begin to bleed, there is an unpleasant smell from the mouth. This disease affects both children, as well as adults. However, stomatitis in infants and preschool children is more common, because at this age the mucous membrane of the mouth is more vulnerable.
Stomatitis in infants (as, indeed, in adults) is divided into species depending on the cause that caused it. So, one of the most common types of stomatitis in infants - candidiasis stomatitis. It is caused by fungi of the species Candida and in the peopleis more commonly known as thrush in children in the mouth. A characteristic symptom of this kind of stomatitis is white plaque in the oral cavity, which does not pass with time, unlike the plaque after feeding.
Both in infants and in older children are also found viral herpetic stomatitis, otherwise called aphthous stomatitis (aphids are small round or oval ulcers of yellow color with a red rim, appearing in the oral cavity on the second day of the disease).
This kind of stomatitis is caused by the herpes virus. Usually it is accompanied by lethargy, fever, a rash on the lips, sometimes - a cough, a runny nose. But the main symptom of viral herpetic stomatitis - the already mentioned above aphthae.
However, aphthous stomatitis in infants is not so common, usually it occurs at the age of 1-4 years. Often this form of stomatitis occurs against the background of chickenpox, measles, influenza and other viral infections.
Sometimes parents also have to facestomatitis of microbial origin, arising on the background of sinusitis, pneumonia, sore throat, etc., traumatic stomatitis (the result of injuries to the oral cavity) and allergic stomatitis. Also occurs catarrhal stomatitis, associated with poor oral hygiene.
but at an early stage the symptoms of all types of stomatitis are similar. The child begins to refuse food because of painin the mouth, his sleep gets worse, the temperature rises. On the mucous membrane of the mouth there are redness, ulcers, plaque, there is an unpleasant smell from the mouth.
How to treat stomatitis in infants? The biggest mistake that young parents can make is resorting to home stomatitis treatment with "grandmother's methods." In no case can you independently handle the baby's mouth with antiseptics, for example, green or peroxide of hydrogen! This can cause a burn of the mucosa and further aggravate the situation.
therefore at the first symptoms of stomatitis it is necessary to show the child to the doctor. Treatment of stomatitis in a child should beis aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. If stomatitis is caused by an infectious disease, you must first cope with the infection. And in the case of candidal stomatitis, it is necessary to fight Candida fungus.
Usually doctors practice an integrated approach. Prescribe pain medication tothe child was able to eat and sleep normally, as well as drugs that accelerate mucosal healing and relieve edema, drugs to eliminate the underlying disease and the means to strengthen immunity.
Like most other diseases, stomatitis in infants is easier to prevent than treat. It is very important to strengthen the immunity of the child withthe earliest age and carefully monitor the oral hygiene of your baby. You also need to minimize the risk of micro-trauma and burns to the mucosa, which can occur, for example, due to hot food or too hard nipples.
Stomatitis in infants is a very unpleasant disease, which can be quite difficult. Do not rely on the treatment of stomatitis in the home folk remedies, be sure to consult a doctor who will prescribe the most effective treatment regimen, depending on the type of stomatitis and severity of the disease.