How to treat otitis in the home?

Otitis is called ear inflammation, which, independing on which of the ear sections is affected, is divided into 3 types: external, middle and inner. The most common otitis media is the middle ear. How to treat otitis in the home? How to prevent the onset of otitis media? The Country of Soviets will tell about this.
Types and symptoms of otitis
Otitis is called any ear inflammation. Before treating otitis media at home, it is important to correctly determine which type of otitis media was encountered. An exact diagnosis can be made only by a doctor, but if there is no possibility to consult a doctor right away, you can determine for yourself whether the inflammation of the external, middle or inner ear has affected the symptoms of the disease.

External otitis media
Otitis externa is an inflammation of the auditory canal. Sometimes it occurs in the form of a furuncle in the ear, but more often the inflammation captures completely the entire skin in the ear canal and the tympanic membrane.
Symptoms of external otitis media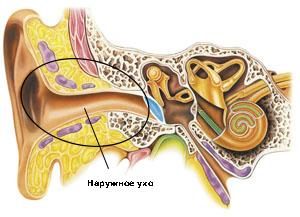
itching in the ear, followed by a bursting pain
strong pain of a pulling character, "shoots in the ear"
pain intensifies by pressing on the base of the auricle or pulling the ear back
pain is exacerbated by chewing and opening the mouth
ears pawn from time to time, sometimes the stuffiness is constant
edema and redness of the auditory canal
swelling in the parotid region
fever
sometimes - a headache
when the boil is opened, the pus flows from the ear
Important! Otitis externa is always the result of getting into the earinfection, that is, bacteria or fungi. Most often, the infection penetrates into the ear while bathing with dirty water, so the popular name for external otitis is the swimmer's ear. Too frequent cleaning of the ears is not designed for this purpose - pins, matches, cotton buds - deprives you of a protective layer of earwax and injures the skin, opening the way for infection.
Average otitis media
Middle otitis media is called a variety of inflammationsthe middle ear, that is, the cavity between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear. As a result of inflammation, this cavity is filled with fluid or even pus, which leads to a decrease in hearing. In children, otitis media is much more common than in adults, especially if they lack vitamin A.
Symptoms of otitis media:
persistent acute pulsating pain in the ear
pain gives to the temple, to the back of the head, to the teeth
permanent stuffiness of the patient ear
hearing loss
elevated temperature, often up to 39 degrees
noise in ears
resonance in the ear of your own voice
an increase and soreness of the behind-the-back lymph nodes
Strong headache
in children - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
discharge from the ear of blood and pus
reduction of pain after the ear begins to leak out of the ear
Important! Most often the infection enters the middle earfrom the outside, but from the inside, through the nose and the auditory tube. This can occur with flu, sore throat, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory infections, sinusitis and any other diseases of the throat and nose, as well as infectious diseases such as measles, rubella, scarlet fever. Usually, the infection gets into the middle ear during a strong cough and sneezing. There is a sharp increase in the risk of getting middle otitis media, if you blow your nose wrong - through both nares at the same time.
Internal otitis media (labyrinthitis)
If otitis media is not treated, infection canpenetrate further into the inner ear. Internal otitis (labyrinthitis) is the inflammation of the labyrinth, that is, the inner ear. This is a rare, but serious disease that can lead to a complete loss of hearing. At home, internal otitis can not be treated. Depending on the severity of the condition, hospitalization may be required, and in most difficult situations, perhaps, surgical intervention.
Symptoms of internal otitis media
severe dizziness, usually 1-2 weeks after an infectious disease
nausea
vomiting
involuntary trembling of the eyeballs - nystagmus
a sense of balance
noise in the ear
hearing loss
Important! Typically, the labyrinthite does not arise by itself, butis a complication of other diseases. Infection can penetrate the labyrinth and cochlea through the middle ear, the meninges, through the blood, and also as a result of trauma. The most dangerous in this sense are such diseases as untreated suppurative otitis media, middle ear tuberculosis, meningitis, influenza, acute respiratory infections, bacterial infections.
Treatment in the home of external and middle otitis media
If there is no possibility to turn toA qualified otolaryngologist can treat otitis media of the external or middle ear independently. But it is important to remember that the trip to the doctor is not canceled in any case, even if all the symptoms of the disease have disappeared. It is necessary, at least, to make sure that the disease is really eliminated and the ear is healthy.
How to treat otitis externa at home?
Usually treatment is local: in the external auditory meatus, gauze turundas moistened in alcohol (70% solution) are introduced, a warming compress is applied on the ear. In case of extensive inflammation, it is necessary to clean the external auditory meatus with a solution of furacilin or boric acid. In acute external otitis media, antibiotics and sulfonamides can also be used, but only with the permission of the doctor.

The most common treatment for externalotitis - ear drops and ointments. However, not all of them can be started on their own, most ear drops also contain antibiotics, and only a few drops and ointments have an antifungal effect. Before consultation with a doctor, you can use only external antiseptic drugs - miramistin, boric alcohol, furacilin.
Important! It is impossible to determine by itself what is causedotitis externa with bacteria or fungus. Antibiotics destroy only bacteria, but are absolutely harmless for fungi and viruses. Any fungal inflammation with antibiotics is greatly enhanced, because the drugs are usually killed by competing microorganisms with fungi. Therefore, do not prescribe antibiotics to yourself: to understand whether they will bring you benefit or harm, only a doctor can.
How to treat otitis media of the middle ear at home?
It is necessary to observe the bedmode, do warming compresses. To reduce the pain syndrome, it is possible to instill 96% alcohol into the diseased ear, but this should only be done before the appearance of pus. At the beginning of the disease, non-antibiotic analgesic ear drops are effective - otinum, otypax, otilabrax, otisol.
Important! In the first two days of otitis treatment, the doctor is often notprescribes antibiotics, they will be needed only if there is no improvement in this time. But the painkillers use both local action and the means for ingestion.
If it's been 3 days since the start of treatmentappointed antibiotic by the doctor, and the pus did not start to separate and the pain persists, then most likely, a procedure such as paracentesis will be needed. This is a small incision on the tympanic membrane, which only a doctor can do, so that the pus that accumulates in the middle ear can come out. After recovery, this incision is completely overgrown, by ear it does not affect.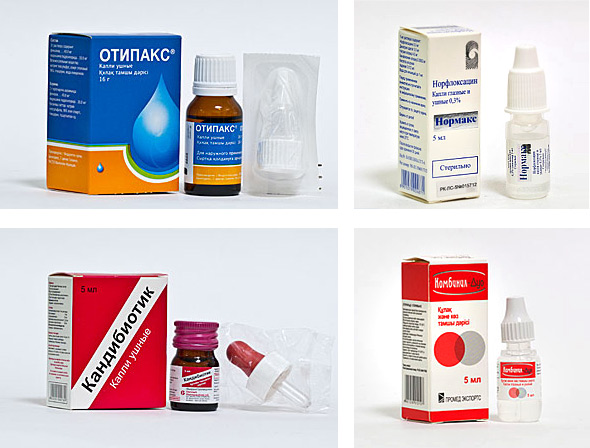
After the appearance of pus continue to treat otitisof the middle ear follows with the help of antibacterial drops - such as sfradeks, otofa, normax, tsipromed, etc. If otitis media has become a complication of the common cold, then vasoconstrictive drops in the nose should also be used.
Important! After the pus begins to separate from the ear,you can no longer use anesthetic drops. They contain alcohol, compounds of salicylic acid and phenazone - all this is extremely harmful to the middle and inner ear.
With the right approach, otitis media for the middle ear should be treated on average 10-14 days.

The causes, diagnosis and treatment of otitis in children: a video tutorial
Children get otitis media very often, much more often than adults. Watch the video and find out how to determine if your child is sick with otitis and what to do in this case.