Vegeto-vascular dystonia: symptoms and treatment

Diagnosis "Vegetative-vascular dystonia" or, abbreviated, the VSD to date, even children put. What is this disease? What are the symptoms of VSD? How to treat VSD? These and other questions will be answered by the Country of Soviets.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia is a violation of the work (dysfunction) of the autonomic nervous system (VNS). The autonomic nervous system is responsible formaintenance of internal balance in the human body, influencing all organs and systems of organs. Violations of the VNS function are manifested most often in the form of violations of the function of blood circulation, digestion, heat exchange.
The term VSD is used in its practice only by physicians of the CIS countries, in the Western countries the concept of vegetative-vascular dystonia is absent.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia: causes
Factors contributing to the development of the IRR are divided into internal and external. Internal factors are factors,predisposing to the onset of the disease: congenital features of the nervous system, periods of hormonal changes in the body, diseases of internal organs, endocrine system, nervous system.
External factors VSD - are the causative factors, they provoke the development of the disease under "suitable" conditions. These factors include: acute infectious diseases, acute and chronic stresses, chronic intoxications, brain injuries, excessive consumption of alcohol.
Is manifested VSD paroxysmal attacks or the symptoms are permanent. Constant symptoms are typical for VSD caused by congenital instability of the nervous system.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia: symptoms
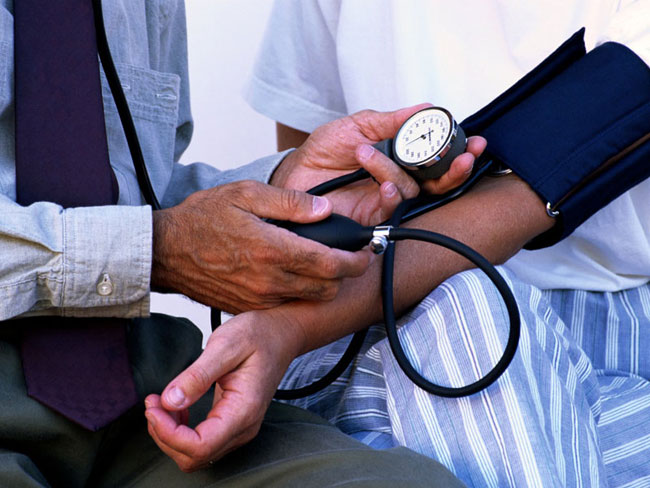
To define vegetative-vascular paroxysms (attacks) it is possible on the following clinical picture: headache or pain in the heart,rapid pulse, palpitations, increased blood pressure and body temperature. In some cases, attacks of the VSD are characterized by general weakness, dizziness, sweating, nausea, lowering of blood pressure and heart rate.
The duration of an attack of the VSD can reach from a few minutes to two or three hours. In most cases, such attacks go by themselves, without treatment.
Exacerbation of the constant IRR is manifested by numbness in the fingers, tingling in the extremities, severe blanching, or vice versa, with cyanotic limbs. The patient's sensitivity to cold increases.
It is only the doctor who can diagnose "vegeto-vascular dystonia". Vegeto-vascular dystonia is divided into 3 types, depending on the reaction of the cardiovascular system:
- cardiac type
- antihypertensive
- hypertensive
The reason for concern should be the availability ofthe patient has such symptoms as: weakness, fatigue, heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, arrhythmia), a feeling of difficulty breathing. These symptoms can signal a cardiac type of disease.
With antihypertensive IRR low systolic blood pressurepressure (less than 100 mm Hg), muscle weakness, headaches, a tendency to fainting. The skin of the limbs is moist, pale, the extremities themselves are often cold.
Hypertensive vegetative-vascular dystonia characterized by such symptoms: increased blood pressure in the absence of symptoms typical of hypertension, palpitation, fatigue.
For VSD, there are obvious functional disturbances in the work of organs and systems without violations of organic: subjective complaints of patients VSD prevail over objective manifestations.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia: treatment
Cure vegetative-vascular dystonia is possible, onlycompletely eliminating the cause that caused this disease. In addition, treatment of specific cardiac syndromes in each individual case should also be carried out within the overall treatment of the VSD.
If you suspect a vegetative-vascular dystonia, you should first contact a psychotherapist who will prescribe the necessary tests and examination, and then make a diagnosis.
Independent symptomatic treatment VSD is dangerous, because the disappearance of one symptom does not mean a complete cure. It is necessary to apply for treatment to a doctor and follow his recommendations faithfully.