Registry Defragmentation

Most Windows settings and settingsare stored in the system registry. Unfortunately, the Windows registry, like any other information stored on the hard disk, is subject to fragmentation, which degrades system performance. In such cases, registry defragmentation.
The Windows registry contains information and settings for programs and hardware, user profiles, etc. The registry records most of the changes made to the system. Wherein part of the registry data is generated during the boot process of the operating system, and some are stored on the hard disk as files. Like any other files, the registry files are subject to fragmentation.
If the registry files are fragmented, access to the system registry slows in proportion to the degree of fragmentation of files. This affects system performance in thewhole. To solve this problem will help defragment the registry. However, it needs to be done correctly, because an ungrammatical defragmentation of the registry can lead to malfunctions in the system. It is even possible that the operating system will have to be reinstalled.
First, you need to remember that defragmentationregistry and defragment the hard drive - this is not the same thing. If you decide to defragment information on the hard disk, this will not have a significant effect on the registry. Registry defragmentation should be done separately using special programs. There are a huge number of applications for defragmenting the registry, both paid and free.
To defragment the registry, you can use different programs, for example:
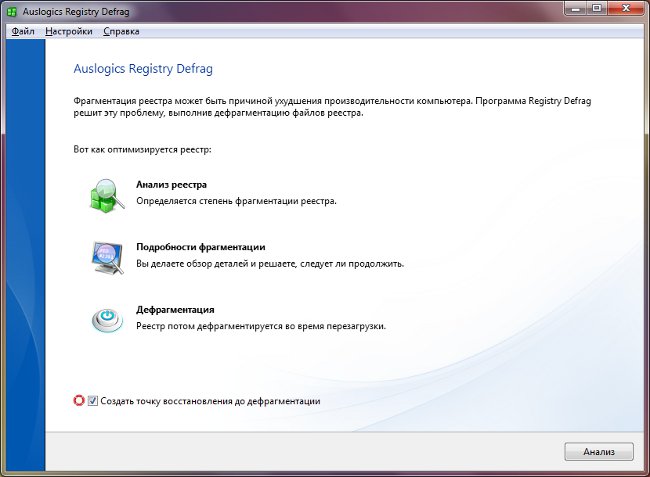
Auslogics Registry Defrag;
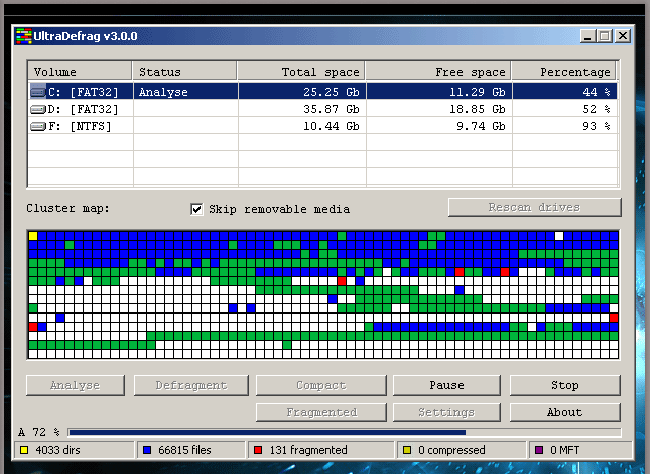
System File Defragmenter;
Defraggler;
QuickSys RegDefrag;
Chemtable Software Registry Life.
Of course, this is not a complete list of defragmenters. Often the function of defragmentation is included in the list of functions of tweaking programs (utilities for fine-tuning the operating system and / or software).
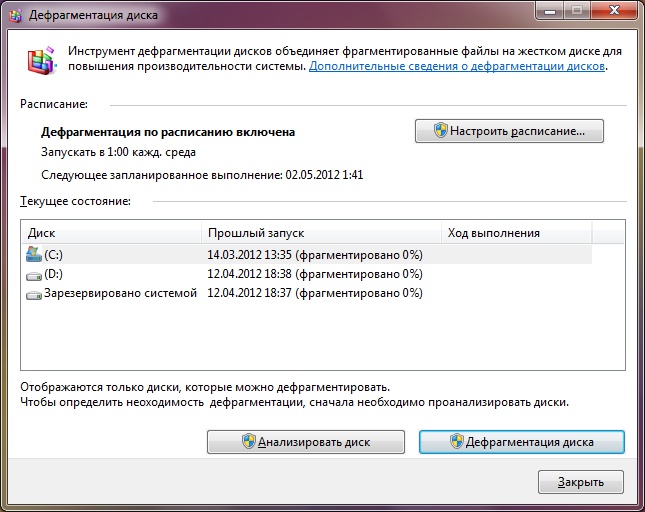
In principle, in all these programs, the registry defragmentation is performed according to the standard scheme. To start, the utility scans the registry to determine the degree of fragmentation. Because the registry defragmentation requiresyou will most likely be offered two options: to defragment the registry immediately and restart the computer or to defragment the registry the next time you reboot.
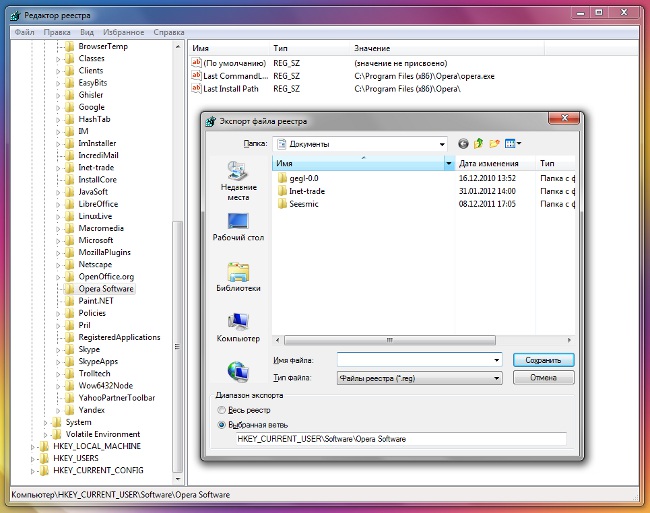
It is advisable to select a program that creates a rollback point before defragmenting (backup the registry) or create such a copy manually to restore the Windows registry from it, if something goes wrong during the defragmentation.
How long does it take to defragment the registry? It depends on several factors. First, at the time of defragmentation affects the number of entries in the registry and the degree of its fragmentation. An important parameter is the speed of reading / writing your hard disk. Also, the defragmentation time depends on the defragmenter itself. The defragmentation process can not be interrupted: Unfinished registry defragmentation can lead to system crashes.
Some programs have option to automatically defragment the registry every time the system boots. This helps to prevent too muchfragmentation of the registry: the best way to combat slowing access to the registry is to prevent fragmentation. However, if necessary, this option can be turned off at any time.
but fragmentation of the system registry is not the only factor that can slow down the work with the Windows registry. Over time, theirrelevant and incorrect keys (records), which increase its volume, in other words - clutter up the registry. Therefore, along with defragmentation, you need to periodically clean the registry of obsolete keys.
Periodic defragmentation of the registry will help improve the speed of the system. However, it needs to be done wisely, becausedamage to the system registry due to improper defragmentation is not so easy to fix, especially if you did not make a backup copy. So use only proven programs for this purpose and do not interrupt the defragmentation in the middle.