Hard Drive Protection

A hard disk is one of the most important components of a computer system, because it is he who is responsible for the long-term storage of information. therefore hard drive protection from mechanical damage and program failures - the number one task in maintaining its efficiency.
A hard disk is a very complex electronic-mechanical design. But, considering its device in a simplified way, we can say that The hard drive consists of three main nodes: magnetic disks, reading magnetic heads and controlling microcircuit. The failure of one of these nodes entails the breakdown of the entire hard drive and, as a consequence, the loss of data.
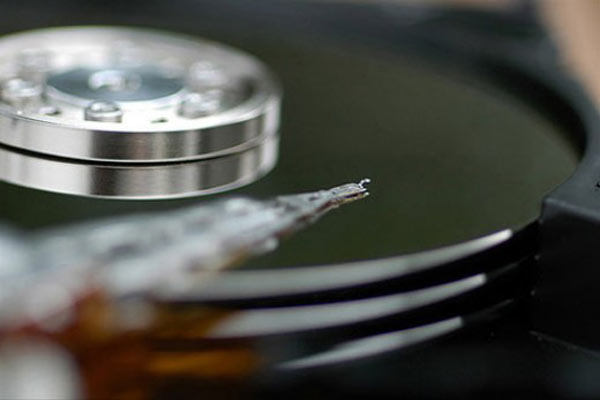
How does the hard disk work? is as follows. On a block of disks made of aluminum or ceramic and coated with a thin ferromagnetic layer, information is recorded and read with the help of magnetic heads.
The disks are fixed to the spindle, which rotates withhigh speed, thereby creating an air cushion between the working surface of the disk and the magnetic read / write head. Such a cushion protects the disc from mechanical contact with the head, because in case of impact, the surface of the ferromagnetic coating is damaged, which can lead to data loss in this sector of the hard drive.
In order to avoid this, it is necessary to observe basic rules for protecting the hard drive.
Rule one - comply with temperature conditions. Temperature too high or too lowis capable of exerting a very large influence on the performance of the hard disk, as the microgeometric parameters of the hard disk plates change under the influence of temperature. And although manufacturers of modern hard drives have made every effort to reduce this effect to zero, it is still undesirable to exceed the upper limit of the working temperature of the hard disk, which is 55-60 ° C.
A hard disk is a device with passive cooling, therefore for free air circulation it is necessary to provide sufficient clearances between the hard disk and the housing components. Wherein it is desirable not to place the hard drives close to each other, next to the video card, optical drives or other elements that actively produce heat. In addition, it is desirable that the area of contact between the hard drive and the metal components of the housing is sufficiently large - this will ensure the transfer of heat to the housing.
To install active devicescooling hard drive should be in extreme cases, very carefully and carefully approaching this issue. The fact is that the vibration from the cooler installed on the hard drive can be no less harmful to the drive than the high temperature. With increased vibration, the time to search for the desired track increases, the load on all nodes of the hard drive grows, and as a result, the life of the hard disk is significantly reduced.
Protect your hard drive from bumps and shocks - one of the main conditions for the correct handling ofhim. A shock on the hard drive can lead to a deflection of the head from its position, as a result of which the so-called head cotton happens - after returning to its original position, the head hits the surface of the disk and damages the ferromagnetic coating. Such a danger threatens mainly the working hard disk, because in the disconnected state, the magnetic heads of modern hard drives are parked - automatically out of the surface of the disks.
In addition to mechanical protection of the hard disk, it is also necessary to provide it surge protection. A sudden increase in voltage causes a sharpincreasing the temperature of the hard drive elements and can lead to overheating of the control chip. Therefore, care must be taken to supply the computer system with a functioning power supply of the required power, as well as an uninterruptible power supply that will insure the computer in the event of unexpected power outages.
Unfortunately, even with all the precautions andprotection rules, it is not always possible to protect the hard disk from the occurrence of malfunctions. This may be due to improper selection of computer equipment, poor-quality parts, too high a load on the system. therefore The most reliable way to hedge against the loss of valuable data is to back up data to third-party drives, for example, to other internal or external hard drives, DWD or CD-ROM drives, flash drives.